DRY CLIMATE
There are two types of dry climate, one is dry arid and the other is dry semiarid . The dry arid (desert) is a climate that covers almost 12 % of the land surface and is popular for its xerophytic vegetation. The dry semiarid which is also known as steppe is mainly a grassland weather condition which covers 14% of the land surface.
PAKISTAN:
These are an example of some of the very earliest forms of ventilation, they are from Hyderabad, founded in 1768 by Ghulam Shah. They used a very simple form of ventilation, triangluar structure, almost like chimneys are on top of the homes and are used to funnel cool breezes in.
Once the most striking feature of Hyderabad was its peculiar skyline dominated by wind-catchers. These wind catchers or Manghu, as they are called in the local Sindhi language, were fixed on housetops, to catch the southwesterly breeze in the hot summer days and evenings. The breeze entering the wind-catchers would penetrate into the room and keep it cool. Due to the numerous wind catchers, Hyderabad be-came famous as manghanjoshaharuor the city of wind catchers.
IN SUMMER: the residents would open the shutter before sunset at 5:00 pm and close the shutter the next day around 11:00 am. In the summer the wind comes from the southwest so the manghface the wind direction.
IN WINTER: they do the opposite, they opened the shutter around 11am and closed it around 3pm. This meant they got the hot daylight from the sun in the south and the wind that comes from the north
For more information on wind catchers click HERE.
These are an example of some of the very earliest forms of ventilation, they are from Hyderabad, founded in 1768 by Ghulam Shah. They used a very simple form of ventilation, triangluar structure, almost like chimneys are on top of the homes and are used to funnel cool breezes in.
Once the most striking feature of Hyderabad was its peculiar skyline dominated by wind-catchers. These wind catchers or Manghu, as they are called in the local Sindhi language, were fixed on housetops, to catch the southwesterly breeze in the hot summer days and evenings. The breeze entering the wind-catchers would penetrate into the room and keep it cool. Due to the numerous wind catchers, Hyderabad be-came famous as manghanjoshaharuor the city of wind catchers.
IN SUMMER: the residents would open the shutter before sunset at 5:00 pm and close the shutter the next day around 11:00 am. In the summer the wind comes from the southwest so the manghface the wind direction.
IN WINTER: they do the opposite, they opened the shutter around 11am and closed it around 3pm. This meant they got the hot daylight from the sun in the south and the wind that comes from the north
For more information on wind catchers click HERE.
DUBAI:
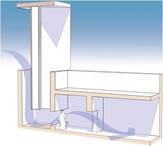
The burj al hawwa, or wind tower was designed for use in dense urban situations where there was a need to draw air down into the compact, courtyard houses. There was no need to use wind towers in qatar, so without the construction of such tall towers they wouldn’t be able to take advantages of the prevailing winds.
The space at the bottom of the tower very importantly filtered the air of sand and dust by collecting any from the wind, before the air was carried into the compound. This was done by the provision of a small step, around 150-300mm in height which caught the heavier grains of sand. The top of the opening between the tower and the distribution room was kept relatively low –about 1500mm this increased the velocity of the prevailing winds.
For more information on the wind towers of Dubai click HERE.
The burj al hawwa, or wind tower was designed for use in dense urban situations where there was a need to draw air down into the compact, courtyard houses. There was no need to use wind towers in qatar, so without the construction of such tall towers they wouldn’t be able to take advantages of the prevailing winds.
The space at the bottom of the tower very importantly filtered the air of sand and dust by collecting any from the wind, before the air was carried into the compound. This was done by the provision of a small step, around 150-300mm in height which caught the heavier grains of sand. The top of the opening between the tower and the distribution room was kept relatively low –about 1500mm this increased the velocity of the prevailing winds.
For more information on the wind towers of Dubai click HERE.
EGYPT:
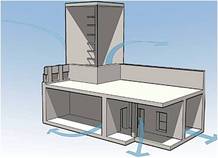
MUD DOME HOUSES are small domes which are made of sun dried bricks, they work very well in hot dry climates such as Egypt. The hot air escapes through small vents in the structures, the vents also allow a small amount of light to enter in, the structures are built in very close proximity to each other and have narrow alleys between them that enable them to shade each other, they also have courtyards which provide an outdoor sleeping area.
BEEHIVE HOUSES are designed to be ideal for desert climates, they have many ways to keep the hot humid climate out of the home. They are made of thick mud brick which traps in the cool whilst keeping out the sun. The high domes collect hot air which keeps it away from the residents sleeping at the bottom of the house.
The dome serves 2 purposes, the first is to collect the hot air and keep the interior cool, the second is the shed rainfall instantly from the exterior. The thick roof an wall is excellent at keeping the inside cool, keeping it between temperatures of 85 to 75 °F. outside temperatures range from 140 to 60°, so it is very important to keep the interior cool.
For more information on mud building construction and properties click HERE.
MUD DOME HOUSES are small domes which are made of sun dried bricks, they work very well in hot dry climates such as Egypt. The hot air escapes through small vents in the structures, the vents also allow a small amount of light to enter in, the structures are built in very close proximity to each other and have narrow alleys between them that enable them to shade each other, they also have courtyards which provide an outdoor sleeping area.
BEEHIVE HOUSES are designed to be ideal for desert climates, they have many ways to keep the hot humid climate out of the home. They are made of thick mud brick which traps in the cool whilst keeping out the sun. The high domes collect hot air which keeps it away from the residents sleeping at the bottom of the house.
The dome serves 2 purposes, the first is to collect the hot air and keep the interior cool, the second is the shed rainfall instantly from the exterior. The thick roof an wall is excellent at keeping the inside cool, keeping it between temperatures of 85 to 75 °F. outside temperatures range from 140 to 60°, so it is very important to keep the interior cool.
For more information on mud building construction and properties click HERE.