MITTAL CHILDREN'S MEDICAL CENTRE BY LLEWELYN DAVIES YEANG
GREAT ORMAND STREET HOSPITAL, LONDON, ENGLAND
PROJECT: Due to be completed in 2012, this mixed-mode ventilation building covers a gross internal floor area of 13,680 square metres, and has a predicted annual CO2 emissions/square metre of 99kg with a NEAT excellence of 77%.
It is important in a hospital for the environment to be comfortable for its occupants at all times. This means ensuring that there are sufficient air changes and fresh air available. It is also important, particularly in the present economic climate to ensure that operational costs are low and that the mechanical services are sustainable and economically viable.
The new Mittal Children's Medical Centre designed by Llwewelyn Davies Yeang and due to be completed in 2012 had to take all of these points into consideration.
DESIGN: The design consists of 2 linked buildings with wards, operating theatres, offices and a restaurant. The chosen ventilation system for the patients wards is mixed-mode (a combination of natural and mechanical ventilation) operated by a building management system (BMS) which has the functionality to enable a manual override of the system when required.
During mid-season the upper quarter of the windows is openable to enable fresh air intake, the air being extracted via a mechanical ventilation system in the ensuite bathrooms. The windows may remain closed may remain closed during the summer and winter periods, when chill beams provide comfort control.
It is important in a hospital for the environment to be comfortable for its occupants at all times. This means ensuring that there are sufficient air changes and fresh air available. It is also important, particularly in the present economic climate to ensure that operational costs are low and that the mechanical services are sustainable and economically viable.
The new Mittal Children's Medical Centre designed by Llwewelyn Davies Yeang and due to be completed in 2012 had to take all of these points into consideration.
DESIGN: The design consists of 2 linked buildings with wards, operating theatres, offices and a restaurant. The chosen ventilation system for the patients wards is mixed-mode (a combination of natural and mechanical ventilation) operated by a building management system (BMS) which has the functionality to enable a manual override of the system when required.
During mid-season the upper quarter of the windows is openable to enable fresh air intake, the air being extracted via a mechanical ventilation system in the ensuite bathrooms. The windows may remain closed may remain closed during the summer and winter periods, when chill beams provide comfort control.
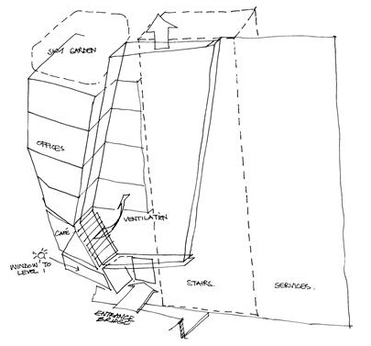
RELATIONSHIP: The relationship between the individual parts of the building is significant to its design.
A glazed vertical ventilation shaft, as well as being a key architectural feature, is also a major aspect of the ventilation strategy.
The chimney serves the ground floor restaurant and also reduces solar gain from the facade. The restaurant itself has mixed mode ventilation with an exposed concrete structure enabling thermal mass.
A glazed vertical ventilation shaft, as well as being a key architectural feature, is also a major aspect of the ventilation strategy.
The chimney serves the ground floor restaurant and also reduces solar gain from the facade. The restaurant itself has mixed mode ventilation with an exposed concrete structure enabling thermal mass.
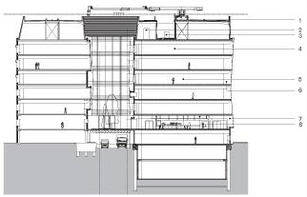
1. Sedum Roof
2. Combined cooling heat and power
3. Absorption
4. Glazed vertical stack evacuates restaurants and solar gains through façade
5. Mixed mode ventilation in wards
6. Balcony with sliding door for cross ventilation
7. Mixed mode ventilation to restaurant
8. Exposed concrete structure in restaurant for thermal mass
2. Combined cooling heat and power
3. Absorption
4. Glazed vertical stack evacuates restaurants and solar gains through façade
5. Mixed mode ventilation in wards
6. Balcony with sliding door for cross ventilation
7. Mixed mode ventilation to restaurant
8. Exposed concrete structure in restaurant for thermal mass